1. Getting started
In this chapter, we will first look at an example with a historical data set and play around with an already trained neural network. We will then take a closer look at the elements of neural networks: artificial neurons. We will see how a single neuron with one input and with two inputs calculates its output.
What are artificial neural networks?
Artificial neural networks receive, process, and output numbers. To start off, a very rough idea is enough to understand the example further down on this page. An artificial neural network consists of many neurons that are connected to each other and are arranged in layers. Each neuron is equipped with a threshold that is represented by a single number (also called bias – which, to simplify here, means the same). The neuron connections also have a number, the so-called weight, representing the strength of this connection (for reasons of clarity, the value of such a connection strength will be symbolised by a specific colour on the following pages). With the help of these numbers, a neural network can store information permanently by changing their values in the course of the so-called training process. During this process, it is trained with data consisting of numbers.
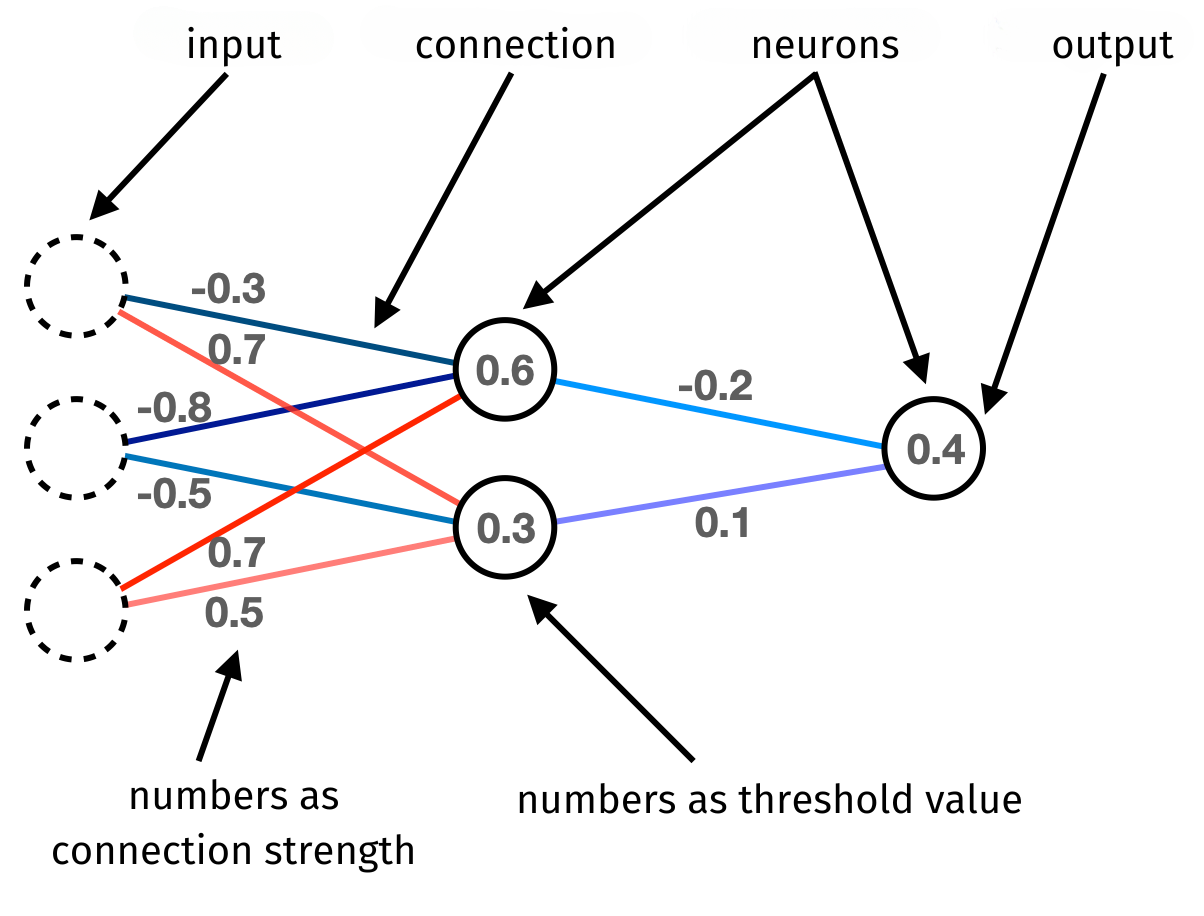
The network adapts during training by comparing its predictions with the actual output data. If the network makes an error, it changes the weights between the neurons to reduce this error. By repeating this process for many examples, the network gradually improves as it learns (only by mathematical algorithms) which connections between the neurons are most relevant for correctly predicting the input data.
Share this page
